Build Your Own Live Crypto Orderbook & Trade Stream with Python
Cryptocurrency has exploded in popularity over the past few years. Major exchanges like Binance process millions of trades every second. If you’ve ever wondered what live crypto market data looks like behind the scenes — this project is a perfect way to see it firsthand.
You’ll learn how to stream:
Real-time order book updates (bids and asks)
Live trade prices and quantities
And store that data neatly into a SQLite database
Code Breakdown & Explanation
Step 1 : Install and Import Required Libraries
import json
import websocket
import requests
from collections import defaultdict
import sqlite3
from datetime import datetime
from datetime import timedeltaStep 2 : Set Global Variables
We define the crypto symbol we want to track, initialize empty data structures for the order book, and variables to track volume and price.
Want to track a different cryptocurrency?
Change this line:
symbol = 'BTCUSDT'
order_book = {'bids': {}, 'asks': {}}
total_volume = 0 # Initialize total traded volume
last_price = None # Initialize last traded price
print_flag = True # Flag to control print sequence
total_bid_qty = 0 # Initialize total bid quantity
total_ask_qty = 0 # Initialize total ask quantityFor example:
- Ethereum to USDT →
'ETHUSDT' - Solana to USDT →
'SOLUSDT' - Dogecoin to USDT →
'DOGEUSDT'
Step 3 : Initialize the SQLite Database
What it does:
Creates a simple SQLite database file (crypto.db) with one table crypto to store our real-time order book data as a JSON string along with a timestamp.
db_name = "crypto.db"
table_name = "crypto"
def initialize_db():
conn = sqlite3.connect(db_name)
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute(f"""
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS {table_name} (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
timestamp DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
Orderbook REAL
)
""")
cursor.execute(f"DELETE FROM {table_name}")
conn.commit()
conn.close()
initialize_db()Why clear old data each time?
We delete existing records so every time you run this code, it starts fresh.
Step 4 : Function to Update Database
What it does:
This function takes our live order book data, converts it to JSON, and inserts it into the database.
def update_db(Orderbook):
conn = sqlite3.connect(db_name)
cursor = conn.cursor()
orderbook_json = json.dumps(Orderbook)
cursor.execute(f"""
INSERT INTO {table_name} (Orderbook)
VALUES (?)
""", (orderbook_json,))
conn.commit()
conn.close()Step 5 : Fetch Initial Depth Snapshot
What it does:
Before streaming real-time updates, we fetch the current state of the order book from Binance’s REST API.
def get_depth_snapshot(symbol, limit=10):
url = f"https://api.binance.com/api/v3/depth"
params = {'symbol': symbol, 'limit': limit}
response = requests.get(url, params=params)
return response.json()We then store those snapshot values:
snapshot = get_depth_snapshot(symbol, limit=10)
for bid in snapshot['bids']:
price = float(bid[0])
quantity = float(bid[1])
order_book['bids'][price] = quantity
for ask in snapshot['asks']:
price = float(ask[0])
quantity = float(ask[1])
order_book['asks'][price] = quantityStep 6 : WebSocket Message Handler
What it does:
This is the heart of the program. It listens for real-time messages from Binance and:
- Updates the bids and asks in our order book.
- Tracks total traded volume and last traded price.
- Stores everything in the SQLite database after every trade and order book update.
def on_message(ws, message):
global total_volume, last_price, print_flag, total_bid_qty, total_ask_qty
message = json.loads(message)
if 'data' not in message:
return
update = message['data']
if 'b' in update and 'a' in update:
u = update['u']
last_update_id = snapshot['lastUpdateId']
if u <= last_update_id:
return
for bid in update['b']:
price = float(bid[0])
quantity = float(bid[1])
if quantity == 0:
if price in order_book['bids']:
del order_book['bids'][price]
else:
order_book['bids'][price] = quantity
for ask in update['a']:
price = float(ask[0])
quantity = float(ask[1])
if quantity == 0:
if price in order_book['asks']:
del order_book['asks'][price]
else:
order_book['asks'][price] = quantity
Time = (datetime.now() + timedelta(seconds=0)).strftime("%H:%M:%S")
order_book['Time'] = Time
total_bid_qty = sum(order_book['bids'].values())
total_ask_qty = sum(order_book['asks'].values())
print_flag = True
if 'p' in update and 'q' in update:
trade_price = float(update['p'])
trade_quantity = float(update['q'])
total_volume += trade_quantity
last_price = trade_price
if print_flag:
Test = [last_price, total_volume, total_bid_qty, total_ask_qty]
update_db(order_book)
print('Done')
print_flag = FalseStep 7 : Define WebSocket URL
What it does:
Here is where it takes your symbol from step 2 to stream the ticker depth and trades. Combines two live Binance streams — order book (depth) and trades (aggTrade) into one WebSocket connection.
depth_stream = f"{symbol.lower()}@depth"
trade_stream = f"{symbol.lower()}@aggTrade"
socket = f"wss://stream.binance.com:9443/stream?streams={depth_stream}/{trade_stream}"Step 8 : WebSocket Callbacks
What it does:
Simple event handlers to print connection status and errors.
def on_open(ws):
print("Connection opened")
def on_error(ws, error):
print(f"Error: {error}")
def on_close(ws, close_status_code, close_msg):
print("Connection closed")Step 9 : Start the WebSocket
What it does:
Connects to the WebSocket and begins listening for live data.
ws = websocket.WebSocketApp(socket, on_message=on_message, on_open=on_open, on_error=on_error, on_close=on_close)
ws.run_forever()Sample Output: SQLite Database and charting
After running your script for a while, open DB Browser for SQLite and look at crypto.db.
You’ll see a table with each order book snapshot stored as a JSON string along with a timestamp.
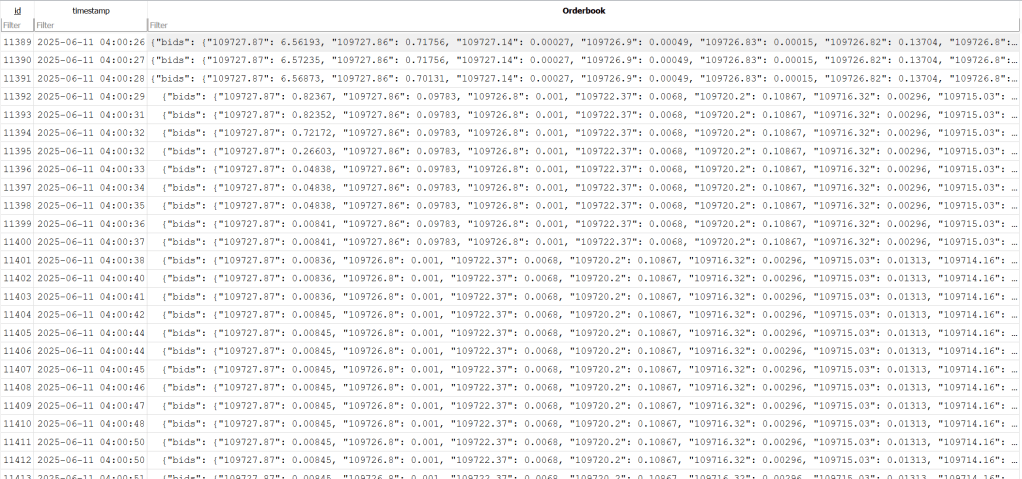
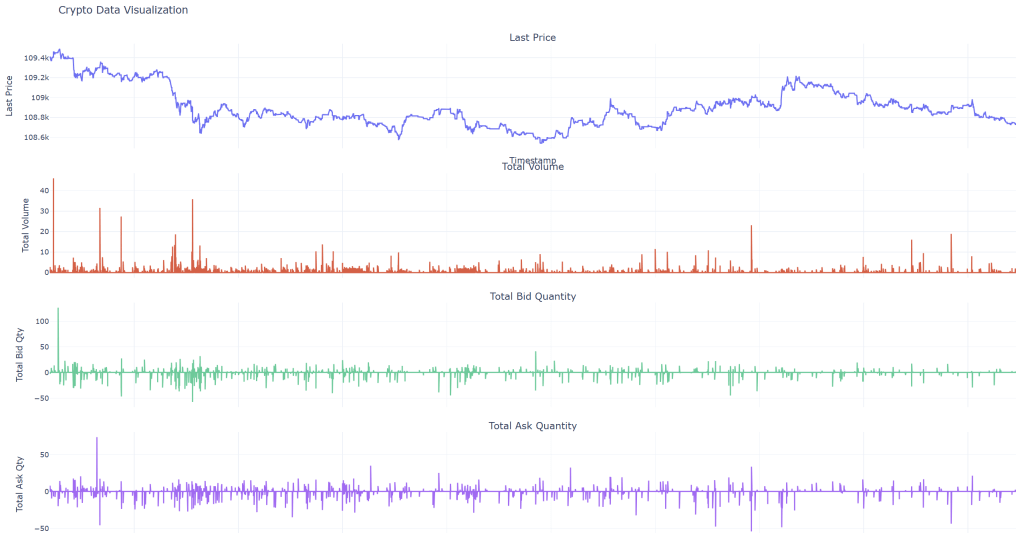
We can now visualize the ticks or perform any analysis to develop strategies for crypto currencies. Happy charting!
Need Help?
I’m always around to help via email. If you get stuck at any step, just reach out — websites can explain only so much, and sometimes a real human helps faster!
