Mind Map
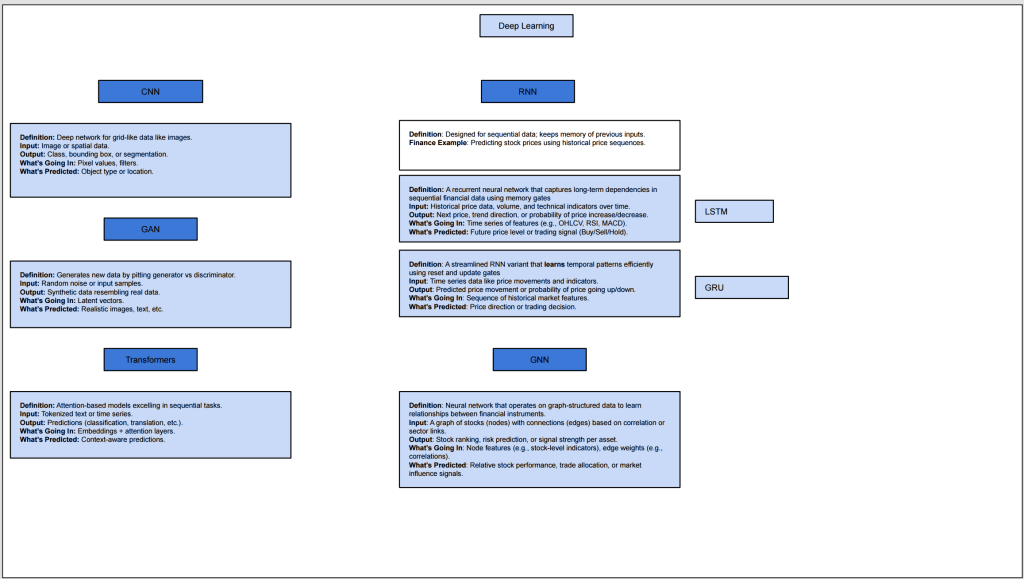
Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of artificial intelligence that enables systems to learn and make decisions from data without being explicitly programmed. In quantitative finance, ML models are pivotal for analyzing vast datasets, identifying patterns, and generating predictive signals. The mind map categorizes ML models into five primary areas: Supervised Learning, Unsupervised Learning, Ensemble Learning, Reinforcement Learning, and Deep Learning.

Supervised Learning
Supervised learning involves training models on labeled datasets, where the input comes with the correct output. The model learns to map inputs to outputs, making it suitable for prediction tasks. Common algorithms include linear regression, logistic regression, support vector machines, and decision trees. In finance, it’s often used for forecasting stock prices or credit scoring.

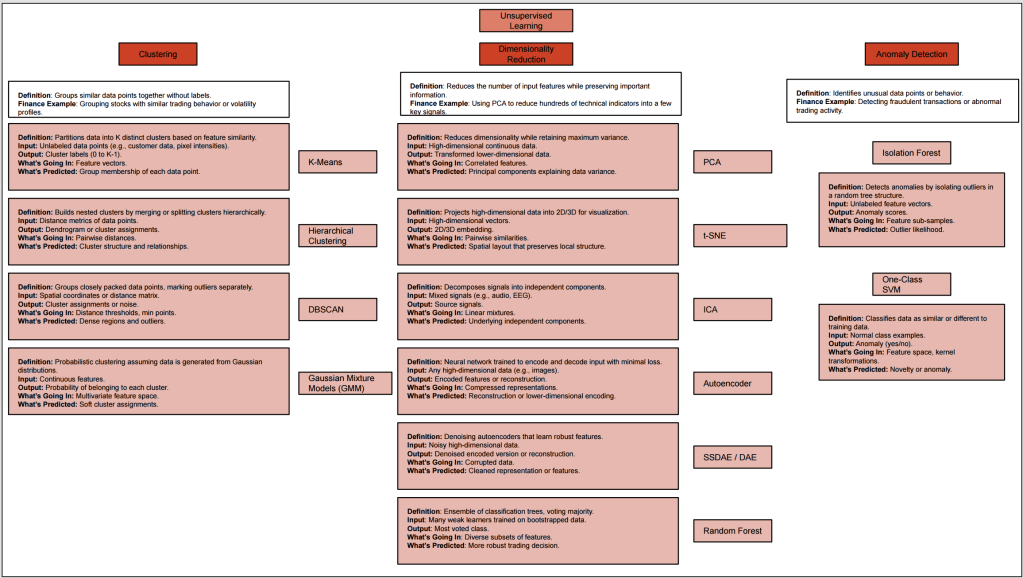
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning deals with unlabeled data, aiming to uncover hidden patterns or intrinsic structures. Techniques like clustering (e.g., K-means) and dimensionality reduction (e.g., PCA) fall under this category. Financial applications include market segmentation and anomaly detection in trading activities.
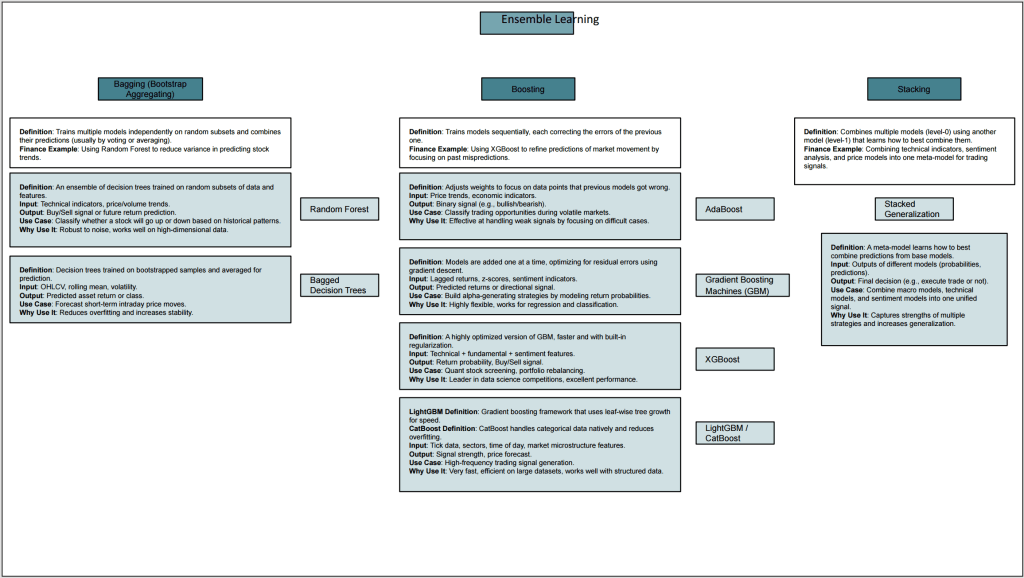
Ensemble Learning
Ensemble learning combines multiple models to improve overall performance. By aggregating the predictions of several learners, ensemble methods like Random Forests, Gradient Boosting Machines, and Bagging enhance accuracy and robustness. In quantitative finance, they help in building more reliable predictive models by reducing variance and bias.
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning is about training agents to make sequences of decisions by rewarding desired behaviors and punishing undesired ones. The agent learns optimal strategies through trial and error. In finance, it’s applied to areas like algorithmic trading, where the model learns to make trading decisions to maximize returns.

Deep Learning
Deep learning utilizes neural networks with multiple layers to model complex patterns in data. It’s particularly effective for high-dimensional datasets. Architectures like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are used for image and sequence data, respectively. In finance, deep learning aids in tasks like sentiment analysis from news articles and time-series forecasting.